The Evaluation of the Speed-Oligo® Mycobacteria Assay for Identification of Mycobacterium spp. from Smear Positive and Negative Sputum Samples by Gülnur Tarhan in Cohesive Journal of Microbiology & Infectious Disease
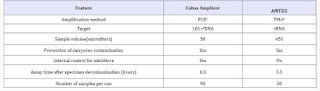
Speed-oligo® Mycobacteria is an oligochromatographic test for the qualitative detection of Mycobacterium genus and the species of M. tuberculosis complex, directly in clinical samples. It is based on polymerase chain reaction targeting 16S rRNA and 16S-23S rRNA regions and double-reverse hybridization on a dipstick using probes bound to colloidal gold and to the membrane. In this study, we evaluated 25 type reference strains of mycobacteria (18 non-tuberculosis mycobacteria, M. tuberculosis H37Rv and M. tuberculosis H37Ra), 60 sputum samples (40 smear positive, 20 smear negative) collected from patient with suspected TB. All results were compared with microscopy, Löwenstein Jensen culture and Inno-Lipa (GenoType Mycobacterium CM/AS; Hain Lifescience, Germany). All smear positive sputum samples were positive with microscopy, culture and Speed-oligo® Mycobacteria. Of 20 smear negative sputum samples, 7 were culture positive. Of 7 culture positive samples, 3 were positive with microscopy and Speedoligo ® Mycobacteria. It is not effective to identify for M. intermedium, M. kansasii and M. xenopi.
For more open access journals in Crimson Publishers,
For more articles in Infectious Disease Open Access Journals,
Follow On Publons : https://publons.com/publisher/6342/crimson-publishers
Follow On Linkedin : https://www.linkedin.com/company/crimsonpublishers